Getting started with R
This section introduces some basic concepts and procedures that help optimize your workflow in R.
Setting up an R session
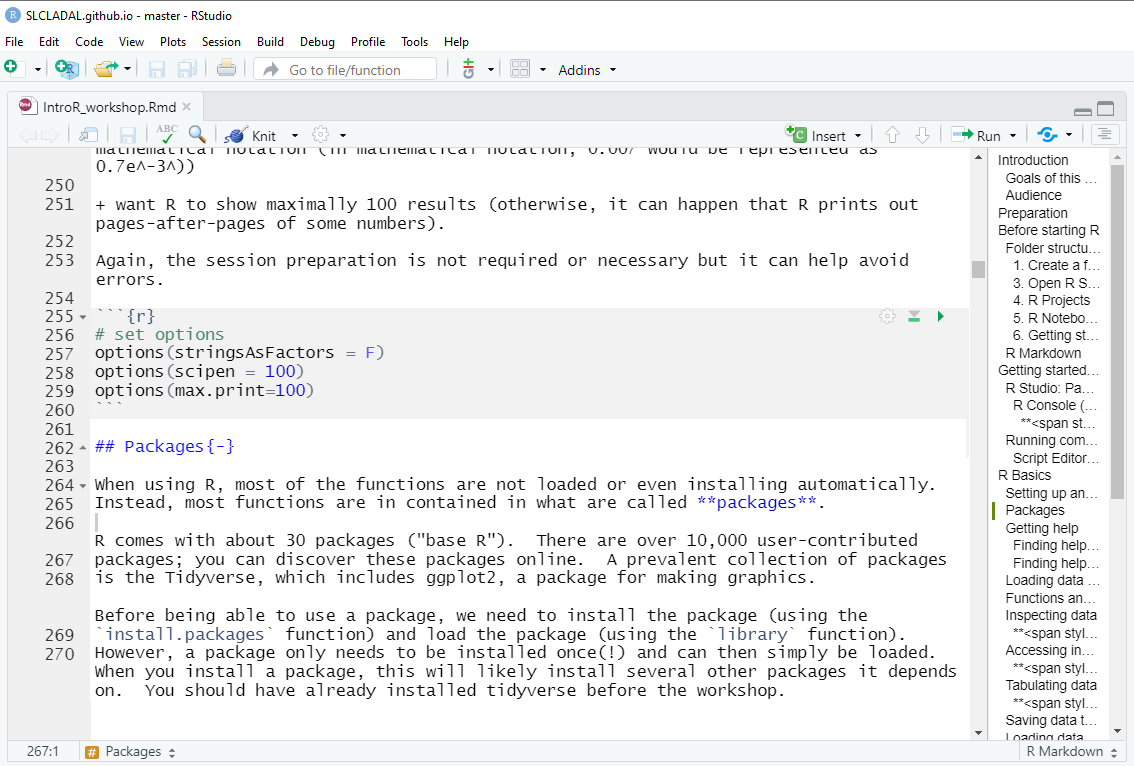
At the beginning of a session, it is common practice to define some basic parameters. This is not required or even necessary, but it may just help further down the line. This session preparation may include specifying options. In the present case, we
want R to show numbers as numbers up to 100 decimal points (and not show them in mathematical notation (in mathematical notation, 0.007 would be represented as 0.7e-3))
want R to show maximally 100 results (otherwise, it can happen that R prints out pages-after-pages of some numbers).
Again, the session preparation is not required or necessary but it can help avoid errors.
In script editor pane of RStudio, this would look like this:
Packages
When using R, most of the functions are not loaded or even installing automatically. Instead, most functions are in contained in what are called packages.
R comes with about 30 packages (“base R”). There are over 10,000 user-contributed packages; you can discover these packages online. A prevalent collection of packages is the Tidyverse, which includes ggplot2, a package for making graphics.
Before being able to use a package, we need to install the package (using the install.packages function) and load the package (using the library function). However, a package only needs to be installed once(!) and can then simply be loaded. When you install a package, this will likely install several other packages it depends on. You should have already installed tidyverse before the workshop.
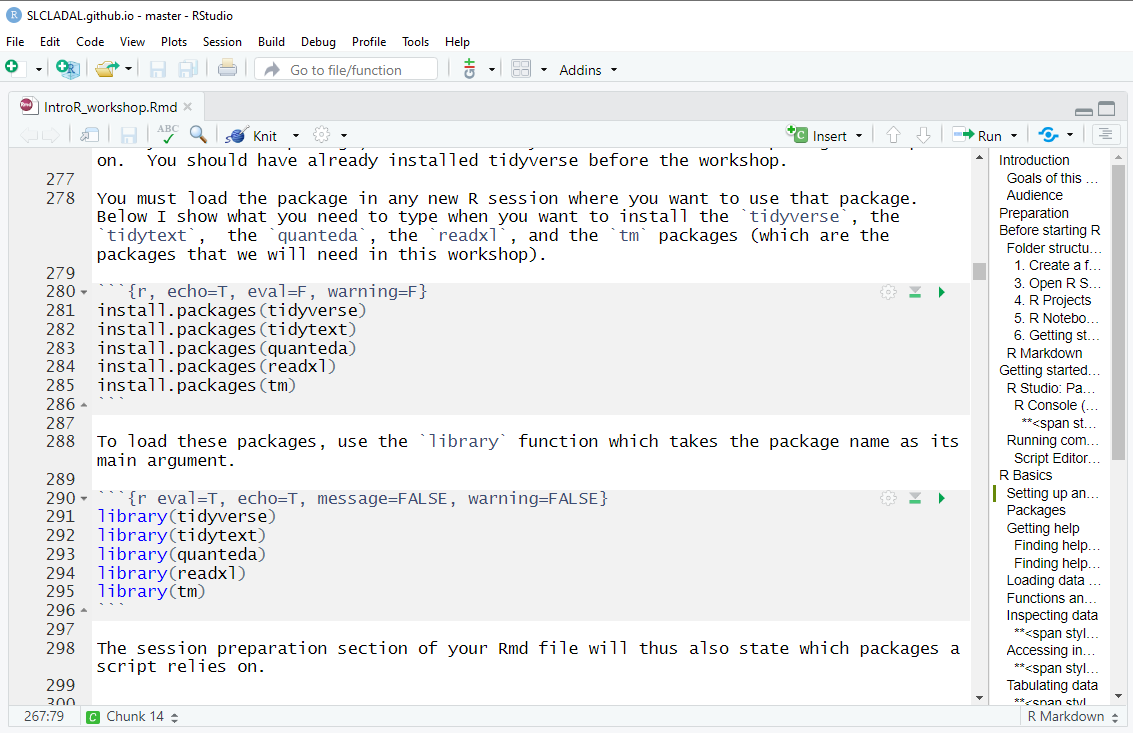
You must load the package in any new R session where you want to use that package. Below I show what you need to type when you want to install the tidyverse, the tidytext, the quanteda, the readxl, and the tm packages (which are the packages that we will need in this workshop).
install.packages("tidyverse")
install.packages("tidytext")
install.packages("quanteda")
install.packages("tokenizers")
install.packages("here")
install.packages("flextable")
# install klippy for copy-to-clipboard button in code chunks
install.packages("remotes")
remotes::install_github("rlesur/klippy")To load these packages, use the library function which takes the package name as its main argument.
library(tidyverse)
library(tidytext)
library(quanteda)
library(tokenizers)
library(here)
library(flextable)
# activate klippy for copy-to-clipboard button
klippy::klippy()The session preparation section of your Rmd file will thus also state which packages a script relies on.
In script editor pane of RStudio, the code blocks that install and activate packages would look like this:
Getting help
When working with R, you will encounter issues and face challenges. A very good thing about R is that it provides various ways to get help or find information about the issues you face.
To get help regrading what functions a package contains, which arguments a function takes or to get information about how to use a function, you can use the help function or the apropos. function or you can simply type a ? before the package or two ?? if this does not give you any answers.
There are also other “official” help resources from R/RStudio.
Read official package documentation, see vignettes, e.g., Tidyverse https://cran.r-project.org/package=tidyverse
Use the RStudio Cheat Sheets at https://www.rstudio.com/resources/cheatsheets/
Use the RStudio Help viewer by typing
?before a function or packageCheck out the keyboard shortcuts
HelpunderToolsin RStudio for some good tips